Measure
The measure tools measure distances, areas, and feature locations on the globe. You can draw a line to measure length, draw a polygon to measure area, or click an individual feature to get measurement information. You can also measure vertical distances.
Measure in the globe
The measure tools are located on the Globe tab. Select a tool and begin measuring in the view. The measure results appear in an on-screen window on the globe.
The measure tools are described in the table below:
|
Measure tool |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Measure Distance |
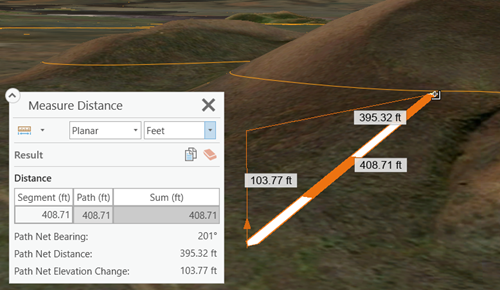
Measure the distance between two or more points. You can measure between locations not on the ground. For example, click a window or face of a building, and measure to another building. The following measurement result values are returned:
|
|
Measure Area |
Draw a polygon to measure the area on the ground. The area measured returns the 2D surface area. |
|
Measure Features |
Measure a feature's length (line), perimeter and area (polygons), or x,y,z location (point features). Note:Result for the topmost feature is returned. To access underlying features, the visibility of any overlapping features must be turned off. |
|
Measure Vertical |
Draw a vertical line to measure height or to measure the vertical difference between two locations. Move the pointer sideways to widen a reference circle at the end of the line to help identify the top (or bottom) of the measurement. |
To use the measure tools, complete the following steps:
In the globe view, on the Globe tab, in the Inquiry group, click the Measure drop-down menu.
Choose a measuring tool.
The measure overlay window appears in the upper left of the view. The measure tools that are 2D or 3D specific are enabled when applicable.
Click in the view to begin measuring. Click to measure a feature, or draw two or more points to measure distances, area, direction, or angles.
Some tools require an initial baseline and then all additional lines are measured from the baseline.
Optionally, in the measure window, set units for the results and the measurement mode.
For units, click the drop-down list and select the unit for the measured result. Only one unit can be displayed at a time. For area and feature measurements, you can set units for different components. For example, you can set the units for the total area as well as the units returned for each segment of the polygon used to calculate the area.
For mode, click the drop-down list to set the interactive measurement type for measuring line distances. Geodesic is the default.
Click the globe as necessary to add any additional segments.
The measure overlay window lists a summary of measured values, for example, when measuring distance, the list includes the distance of each segment, the total path, and the sum of all paths as well as the net direction angle and distance values.
Press Esc anytime during the sketch to cancel a measure to start over, or click Clear Results
 to completely clear and reset the measurement results. Click Copy Results
to completely clear and reset the measurement results. Click Copy Results  to copy and paste the results to use in other applications.
to copy and paste the results to use in other applications.Optionally, in the measure window, switch to another measure tool using the drop-down menu.
Double-click or press F2 to finish the measure sketch and save the results in the measure window until you close the active view.
The measure tool remains active.
Click Close the measure tool
 in the measure overlay window when you are finished measuring.
in the measure overlay window when you are finished measuring.Closing the measure overlay window reactivates the Explore tool
 .
.
Measure distance in the globe
When you use the Measure Distance tool ![]() in the globe, the measured results include visual feedback for multiple components that are returned. The dashed orange-and-white line indicates the direct distance between the current endpoints when you draw segments over the surface. Labels for vertical offset distances and 2D distances also display, where applicable. A dynamic horizontal laser line shows the comparative heights throughout the view. When you hover over the height component arrow, you can constrain distance measurements vertically, meaning measuring stays in the y-direction only as you drag the arrow perpendicular to the first click of the segment. If the mouse moves far enough away from vertical, it returns to measuring in the full 3D distance mode.
in the globe, the measured results include visual feedback for multiple components that are returned. The dashed orange-and-white line indicates the direct distance between the current endpoints when you draw segments over the surface. Labels for vertical offset distances and 2D distances also display, where applicable. A dynamic horizontal laser line shows the comparative heights throughout the view. When you hover over the height component arrow, you can constrain distance measurements vertically, meaning measuring stays in the y-direction only as you drag the arrow perpendicular to the first click of the segment. If the mouse moves far enough away from vertical, it returns to measuring in the full 3D distance mode.
To measure height or the difference between two points, use Measure Vertical ![]() . For example, you can measure the elevation of a mountain or the height of a building.
. For example, you can measure the elevation of a mountain or the height of a building.
To change perspective (pan, zoom, or rotate) while measuring, press the C key to temporarily navigate. Release the C key to continue measuring.
Measurement modes
The measurement mode drop-down list provides the following measurement modes you can use for distance measurements:
|
Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Geodesic |
The shortest line between two points on the earth's surface on a spheroid (ellipsoid). One use for a geodesic line is to determine the shortest distance between two cities for an airplane's flight path. This is also known as a great circle line if based on a sphere rather than an ellipsoid. |
|
Loxodromic |
A loxodromic distance is a line of constant bearing or azimuth. Great circles are often broken into a series of loxodromes, which simplifies navigation. This is also known as a rhumb line. Unlike a geodesic line, it is not the shortest distance between two points. |
|
Great Elliptic |
The line on a spheroid (ellipsoid) defined by the intersection at the surface by a plane that passes through the center of the spheroid and the start and endpoints of a segment. This is also known as a great circle when a sphere is used. The great elliptic type allows you to create lines only. |
Choose the measure units
In the Measure window, only a single measurement unit can be displayed at a time.
When you use the Measure window, you must choose Imperial or Metric units. These options are collections of related units, such as centimeters, meters, and kilometers, that automatically adjust based on the distance or area being measured. As you zoom in or out, the unit updates. For example, in metric units, the result of measuring the width of a road is 15 meters, but measuring between Paris and Rome is 1,100 kilometers without any change to the unit settings.
When you first open the Measure tool, it uses the project's default distance units and area units to determine imperial or metric as the unit of measure. Optionally, use the drop-down menu on the Measure window to change the units.
Constant measure feedback
Instead of interactive measuring, Z-coordinate measurement feedback is always available in the globe, regardless of whether the Measure tool is enabled as you navigate the view. This value is shown at the bottom of the view, next to the coordinate display. The Z-coordinate value indicates the height of the surface or feature at the pointer location. The z-units are determined by the elevation units set for your globe.